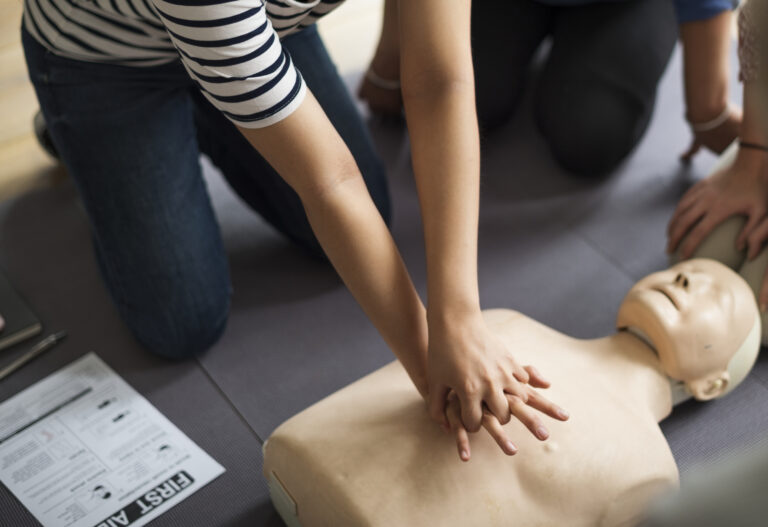
We think that everyone should be familiar with the fundamentals of first aid so that they can care for themselves or other injured individuals in an emergency. Every second matters when it comes to emergency care, even if you’re fortunate enough to call for an ambulance that’s only a few minutes away. Before emergency medical assistance arrives, learning how to stop serious bleeding can greatly increase a person’s chance of making a full recovery and, in some cases, even save their life.
Most people’s first reaction in an emergency is to figure out how to call 911 at the earliest. This is a crucial instinct that should never be ignored, but are you equipped to administer emergency first aid to an injured person or yourself in the moments before help arrives?
If this question puts you in doubt, then maybe it’s time that you should learn First Aid. American HealthCare Academy offers the most flexible and affordable online First Aid training and certification course for working and non-working individuals. It’s 100% online and can be completed anytime anywhere. The videos are comprehensive and clear to understand. The course is instructed by OSHA-certified trainers. You can also download the certificate after completing the course. Get in touch with them on their website today!
Bleeding and Types of Bleeding
So, what is bleeding? It is the loss of blood from the body’s circulatory system. It is often brought on by blood vessel damage or injury. Depending on the source and location of the bleeding, bleeding can be internal or external. It ranges from minor to severe which depends on the injury.
There are various forms of bleeding, such as:
- Internal bleeding: Bleeding within organs or tissues is referred to as internal bleeding. It may not produce obvious symptoms of bleeding and can’t be easily diagnosed.
- External Bleeding: Blood loss from an injury or cut that happens outside the body is referred to as external bleeding. It is completely visible on the body and may need to be treated immediately.
- Secondary bleeding: When an initial wound has stopped bleeding, there can still be secondary bleeding. Infection, the dislodging of a blood clot, or other causes may result in secondary bleeding.
- Bleeding from an artery: Bleeding from an artery that transports oxygen-rich blood away from the heart is referred to as arterial hemorrhage. Bright red bleeding from the arteries can surge in sync with the heartbeat.
- Venous bleeding: Venous bleeding originates in a vein that returns blood to the heart. Venous bleeding can be steady and the blood could be dark red.
- Capillary bleeding: The smallest blood arteries in the body, capillaries, are the source of this type of bleeding. Capillary hemorrhage or bleeding can be gradual and oozing.
First Aid Treatment to Control Bleeding
Following are the steps of the first aid treatment to control bleeding:
- The first step is to apply direct pressure on the wound to stop the bleeding. If the pressure does not stop the bleeding, then you should seek medical attention immediately.
- Other first aid techniques include elevating the wound, using pressure points, and using a tourniquet.
- It is important to note that the use of a tourniquet should only be used in extreme cases, as prolonged use of a tourniquet can lead to tissue damage.
- When using pressure points, the person should apply firm pressure using the fingertips or a piece of cloth to the wound.
- Elevating the wound by raising the arm or leg can help control the bleeding by reducing the flow of blood.
What are The 6 Steps to Control Bleeding?
The following are the six steps to control bleeding:
- Raise the wound above the heart
- Apply direct pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage
- If necessary, use a pressure point
- Apply a clean bandage to the wound
- Contact a doctor if the bleeding is excessive or if the person hasn’t received a tetanus vaccine in the last 10 years
- Scrub the wound with soap and warm water
Home Remedies to Stop Bleeding
Home treatments can be used to assist stop bleeding, including applying pressure with a clean cloth or bandage, covering the area with sterile cotton or gauze, and providing a cold compress to lessen swelling.
Along with using aloe vera or apple cider vinegar, other methods for stopping bleeding include applying a herbal ointment or tea tree oil to the wound. Furthermore, natural astringents like baking soda, witch hazel, or lemon juice can be utilized to halt the bleeding.
Conclusion
If you have significant bleeding or bleeding that won’t stop, you should visit a doctor right once since it could be fatal if you don’t. Staying prepared to handle emergencies with First Aid will help you in giving support to the injured till you reach the hospital. Locate the best First Aid training providers in your area on CPR Care Near Me and enroll now!